
Understanding the Windows Hosts File: A Detailed Guide for You
The Windows Hosts file is a crucial component of your computer’s operating system, serving as a local DNS resolver. It allows you to map hostnames to IP addresses without relying on external DNS servers. In this article, I will delve into the intricacies of the Windows Hosts file, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of its purpose, structure, and usage.
What is the Windows Hosts File?
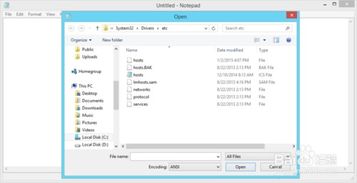
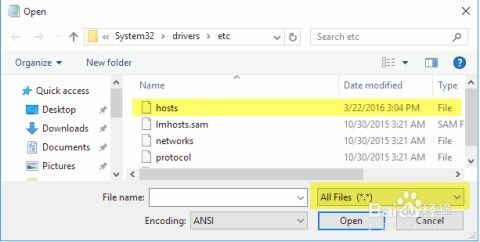
The Windows Hosts file is a plain text file that resides in the C:WindowsSystem32driversetc directory. It contains a list of IP addresses and corresponding hostnames. When you type a hostname into your web browser, the operating system checks the Hosts file first to see if it can resolve the hostname to an IP address. If the hostname is not found in the Hosts file, the operating system will then query an external DNS server to resolve the hostname.
Why Use the Windows Hosts File?
There are several reasons why you might want to use the Windows Hosts file:
-
Speed up DNS resolution: By mapping hostnames to IP addresses locally, you can avoid the delay caused by querying external DNS servers.
-
Block unwanted websites: You can add entries to the Hosts file to block access to specific websites.
-
Test local websites: When developing a website, you can map the hostname to the IP address of your local development server to test the website without needing to set up a separate DNS server.
-
Redirect traffic: You can redirect traffic from one hostname to another by adding an entry in the Hosts file.
Structure of the Windows Hosts File
The Windows Hosts file is structured as follows:
| Line | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | 127.0.0.1 localhost |
| 2 | 127.0.0.1 localdomain |
| 3 | 127.0.0.1 loopback |
| 4 | ::1 localhost |
| 5 | ::1 localdomain |
| 6 | ::1 loopback |
| 7 | Added by Windows Hosts File Manager |
| 8 | ::1 localhost |
| 9 | ::1 localdomain |
| 10 | ::1 loopback |
The first few lines of the Hosts file contain the IP addresses and hostnames for the local machine. The ” symbol is used to add comments to the file. The rest of the file contains the mappings between hostnames and IP addresses.
Editing the Windows Hosts File
Editing the Windows Hosts file is a straightforward process. You can use any text editor, such as Notepad, to open and modify the file. Here’s how to do it:
-
Open Notepad or another text editor.
-
Go to File > Open and navigate to the C:WindowsSystem32driversetc directory.
-
Select the Hosts file and click Open.
-
Make the desired changes to the file.
-
Save the file by clicking File > Save As. Make sure to save the file with the .txt extension.






