
Shapefile Files: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
Shapefile files are a fundamental component in the world of geographic information systems (GIS). They are widely used for storing, managing, and analyzing spatial data. If you are new to GIS or looking to enhance your understanding of shapefiles, this guide is tailored for you. Let’s delve into the intricacies of shapefile files, their types, uses, and how to work with them effectively.
What is a Shapefile?
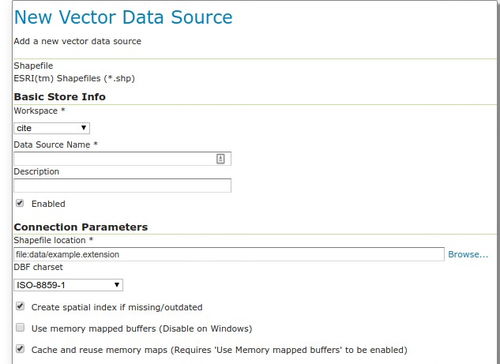
A shapefile is a popular geospatial data format used in GIS. It is a collection of files that work together to represent a geographic area. These files include a point, line, or polygon geometry, as well as attribute data that describes the features. Shapefiles are compatible with various GIS software, making them a versatile choice for data storage and analysis.
Types of Shapefiles
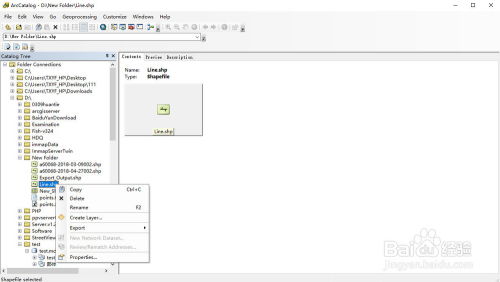
Shapefiles can be categorized into three main types based on their geometry:
| Geometry Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Point | Represents a single location on the Earth’s surface, such as a building or a city. |
| Line | Represents a linear feature, such as a road or a river. |
| Polygon | Represents a closed area, such as a lake or a country. |
How to Create a Shapefile
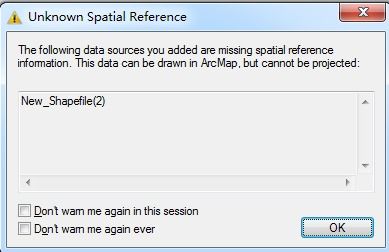
Creating a shapefile involves several steps, including defining the coordinate system, creating the geometry, and adding attribute data. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Choose a GIS software that supports shapefile creation, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, or MapInfo.
- Define the coordinate system for your project. This is crucial for accurate spatial analysis.
- Create the geometry by drawing points, lines, or polygons on the map.
- Add attribute data to describe the features. This can include information such as names, addresses, or other relevant details.
- Save the shapefile, ensuring that all associated files are included.
Using Shapefiles in GIS
Shapefiles are versatile tools for various GIS applications. Here are some common uses:
- Mapping: Shapefiles are used to create maps that visualize spatial data.
- Analysis: GIS software can analyze shapefiles to extract information, such as identifying patterns or calculating distances.
- Geocoding: Shapefiles can be used to convert addresses into geographic coordinates.
- Data Integration: Shapefiles can be combined with other data sources to create comprehensive spatial datasets.
Best Practices for Working with Shapefiles
Here are some best practices to ensure efficient and accurate shapefile management:
- Use consistent coordinate systems across your projects.
- Keep your shapefiles organized and well-documented.
- Regularly update your shapefiles to reflect the latest data.
- Backup your shapefiles to prevent data loss.
Common Challenges with Shapefiles
While shapefiles are a powerful tool, they come with some challenges:
- File Size: Shapefiles can become large and difficult to manage, especially when dealing with extensive datasets.
- Compatibility: Not all GIS software supports shapefiles, which can limit their usability.
- Complexity: Creating and editing shapefiles can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge.
Alternatives to Shapefiles
As GIS technology evolves, alternative data formats have emerged. Some popular alternatives to shapefiles include:
- GeoJSON: A lightweight format for storing and exchanging geospatial data.
- ESRI Shapefile: A newer format developed by Esri, offering improved performance and compatibility.
- Geopackage: A standard format for storing geospatial data, supporting various data types and features.
Conclusion
Shapefile files are an essential tool for GIS professionals and enthusiasts. Understanding their structure, uses, and


