
Distributed File System Replication: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding distributed file system replication is crucial in today’s interconnected world where data availability and redundancy are paramount. By replicating files across multiple nodes, organizations can ensure data integrity, improve performance, and enhance disaster recovery capabilities. This article delves into the intricacies of distributed file system replication, exploring its various aspects and benefits.
What is Distributed File System Replication?
Distributed file system replication is a technique that involves copying files from one node to another in a distributed file system. This process ensures that data is available and consistent across multiple locations, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. By replicating files, organizations can minimize the risk of data loss and improve overall system performance.
Types of Distributed File System Replication
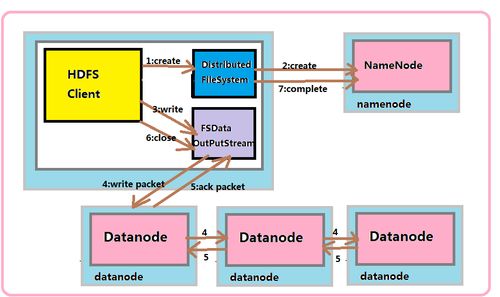
There are several types of distributed file system replication, each with its unique characteristics and use cases. Here are some of the most common types:
-
Asynchronous Replication: In asynchronous replication, data is copied from the source node to the destination node at a later time. This method is suitable for scenarios where real-time data consistency is not critical.
-
Synchronous Replication: Synchronous replication ensures that data is copied from the source node to the destination node simultaneously. This method provides real-time data consistency but may impact system performance due to the additional overhead.
-
Incremental Replication: Incremental replication copies only the changes made to the source files since the last replication. This method is efficient in terms of bandwidth usage and reduces the replication time.
-
Full Replication: Full replication copies all the files from the source node to the destination node. This method ensures that both nodes have an identical copy of the data but may consume more bandwidth and storage space.
Benefits of Distributed File System Replication
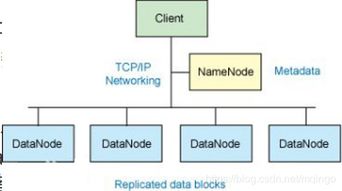
Distributed file system replication offers several benefits, making it an essential component of modern data storage and management solutions. Here are some of the key advantages:
-
Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: By replicating files across multiple nodes, organizations can minimize the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters. This ensures that data remains accessible even in the event of a node failure.
-
Improved Performance: Replicating files to geographically dispersed locations can reduce latency and improve data access speeds for users in different regions.
-
Disaster Recovery: Distributed file system replication simplifies disaster recovery processes by providing a copy of the data that can be quickly restored in the event of a disaster.
-
Data Integrity: Replication ensures that data remains consistent across all nodes, reducing the risk of data corruption or inconsistencies.
Challenges of Distributed File System Replication
While distributed file system replication offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some of the common challenges faced by organizations:
-
Bandwidth and Storage Requirements: Replicating files across multiple nodes requires significant bandwidth and storage resources, which can be costly for organizations with large data volumes.
-
Complexity: Implementing and managing a distributed file system replication solution can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise.
-
Consistency and Synchronization: Ensuring data consistency and synchronization across all nodes can be challenging, especially in environments with high network latency or limited bandwidth.
-
Security: Protecting replicated data from unauthorized access and ensuring secure data transfer between nodes is crucial, especially in highly regulated industries.
Use Cases of Distributed File System Replication
Distributed file system replication is widely used in various industries and applications. Here are some common use cases:
-
Cloud Storage: Cloud service providers use distributed file system replication to ensure data availability and redundancy across multiple data centers.
-
Enterprise Data Storage: Organizations with large data volumes and stringent data availability requirements rely on distributed file system replication to protect their data.
-
Media and Entertainment: Content providers use distributed file system replication to ensure high availability and redundancy of their media assets.
-
Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use distributed file system replication to ensure the availability of patient records and medical images.
Conclusion
Distributed file system replication is




