
Erasing a File: A Comprehensive Guide for You
Managing files on your computer is an essential skill, and one of the most fundamental tasks is to erase a file. Whether you’re cleaning up space, removing sensitive data, or simply organizing your files, knowing how to erase a file correctly is crucial. In this detailed guide, I’ll walk you through the process of erasing a file from various perspectives, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of the task at hand.
Understanding File Deletion
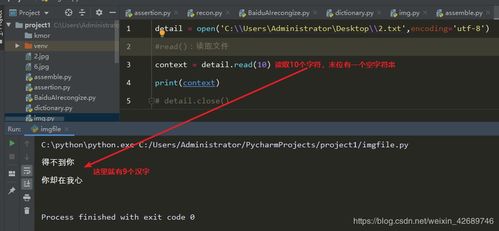
When you delete a file, it doesn’t immediately vanish from your computer. Instead, the file’s data is marked as available for overwriting. This is where the process can get a bit tricky, as there are different methods to ensure that a file is truly and permanently erased.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Trash or Recycle Bin | Files are moved to the Trash or Recycle Bin, where they can be restored if needed. |
| Permanent Deletion | Files are deleted without being moved to the Trash or Recycle Bin, making them more difficult to recover. |
| Secure Deletion | Files are overwritten multiple times to ensure they cannot be recovered. |
Understanding these methods is the first step in erasing a file effectively.
Erasing a File on Windows
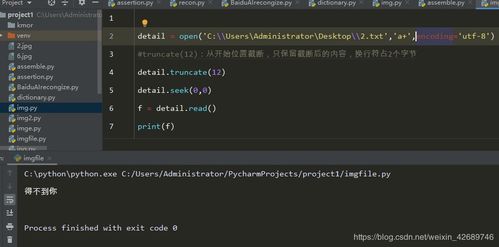
On Windows, there are several ways to erase a file, each with its own level of security and ease of use.
Using the Delete Key
Pressing the Delete key is the most common method to erase a file. When you do this, the file is moved to the Recycle Bin. To permanently delete the file, you can either right-click on the Recycle Bin and select “Empty Recycle Bin” or press “Shift + Delete” to bypass the Recycle Bin and delete the file immediately.
Using the Command Prompt
For a more advanced approach, you can use the Command Prompt. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type “del” followed by the file path. For example, to delete a file named “example.txt,” you would type “del C:pathtofileexample.txt”. To delete multiple files, you can use wildcards, such as “del C:pathtofile.txt” to delete all text files in the specified directory.
Using Third-Party Software
There are numerous third-party software solutions available that offer more advanced features for file deletion, including secure deletion. These tools often provide a user-friendly interface and additional options for managing files and folders.
Erasing a File on macOS
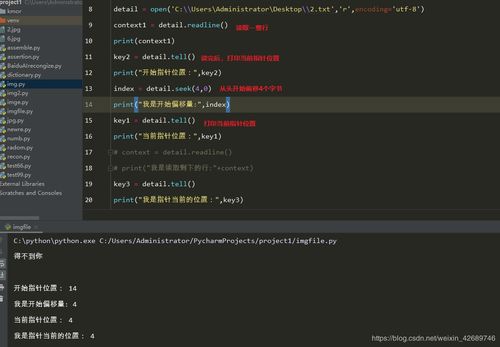
On macOS, the process of erasing a file is quite similar to Windows, with a few differences in terminology and interface.
Using the Delete Key
Pressing the Delete key on macOS will move the file to the Trash. To permanently delete the file, you can either right-click on the Trash and select “Empty Trash” or press “Command + Option + Delete” to bypass the Trash and delete the file immediately.
Using the Terminal
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, you can use the Terminal. Open Terminal and type “rm” followed by the file path. For example, to delete a file named “example.txt,” you would type “rm /path/to/file/example.txt”. To delete multiple files, you can use wildcards, such as “rm /path/to/file/.txt” to delete all text files in the specified directory.
Using Third-Party Software
As with Windows, there are many third-party software solutions available for macOS that offer additional features for file deletion and management.
Erasing a File on Linux
On Linux, the process of erasing a file is quite similar to macOS, with a few differences in the command syntax.
Using the Delete Key
Pressing the Delete key on Linux will move the file to the Trash. To permanently delete the file, you can either right-click on the Trash and select “Empty Trash” or press “Ctrl + Alt + Delete” to bypass the Trash

