
Understanding the Hosts File Location: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered where the hosts file is located on your computer? This crucial system file plays a significant role in managing network connections and DNS resolution. In this detailed guide, I will walk you through the various aspects of the hosts file location, its importance, and how to manage it effectively.
What is the Hosts File?
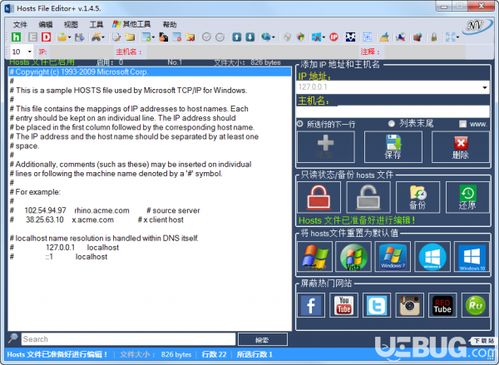
The hosts file is a local database that maps hostnames to IP addresses. It is used by the operating system to resolve domain names without relying on external DNS servers. This file is particularly useful for bypassing DNS lookups, testing local websites, and blocking unwanted websites.
Hosts File Location
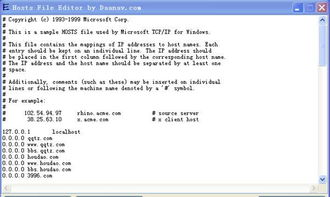
The location of the hosts file varies depending on the operating system you are using:
| Operating System | Location |
|---|---|
| Windows | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| macOS | /etc/hosts |
| Linux | /etc/hosts |
It is important to note that modifying the hosts file requires administrative privileges on Windows and macOS, while Linux users may need root access.
Importance of the Hosts File
The hosts file serves several critical functions:
-
Blocking Websites: By adding unwanted domain names to the hosts file, you can block access to those websites without installing additional software.
-
Testing Local Websites: When developing or testing local websites, you can map domain names to your local IP address to access them directly.
-
Bypassing DNS Lookups: In some cases, you may want to bypass DNS lookups for specific domains, such as when testing a new DNS server or resolving domain names locally.
Modifying the Hosts File
Modifying the hosts file is a straightforward process, but it requires caution to avoid making mistakes that could disrupt your network connectivity.
Windows
1. Open Notepad as an administrator by right-clicking on the Notepad icon and selecting “Run as administrator.”
2. Navigate to the hosts file location (C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts) and open it with Notepad.
3. Make the necessary changes to the file, such as adding or removing domain names and their corresponding IP addresses.
4. Save the file and close Notepad.
macOS and Linux
1. Open a terminal window.
2. Use the “sudo nano /etc/hosts” command to open the hosts file with root privileges.
3. Make the necessary changes to the file, such as adding or removing domain names and their corresponding IP addresses.
4. Save the file and exit the terminal.
Conclusion
The hosts file is a powerful tool that can help you manage your network connections and DNS resolution. By understanding its location and how to modify it, you can take full advantage of its features to improve your online experience.



