
Paging File: A Comprehensive Guide
A paging file, also known as a swap file, is a crucial component of modern operating systems. It allows your computer to use a portion of your hard drive as virtual memory, which can significantly enhance system performance. In this article, we will delve into the details of paging files, their purpose, and how they work. Let’s explore this fascinating topic together.
What is a Paging File?
A paging file is a type of file that is used by the operating system to simulate additional physical memory when the RAM (Random Access Memory) is insufficient. It works by transferring data from RAM to the hard drive, freeing up space in the RAM for other applications. This process is known as swapping or paging.
Why Do We Need a Paging File?

Modern computers have limited physical memory, and running multiple applications simultaneously can quickly consume this memory. When the RAM is full, the operating system needs to find a way to manage the excess data. This is where the paging file comes into play. By using a portion of the hard drive as virtual memory, the operating system can continue running applications without crashing or slowing down.
How Does a Paging File Work?
When the RAM is full, the operating system selects a portion of the data to be moved to the paging file. This process is called a page fault. The data is then written to the paging file, and the corresponding space in the RAM is freed up. When the application needs the data again, it is loaded back into the RAM from the paging file. This process is transparent to the user and happens in the background.
Creating and Managing a Paging File
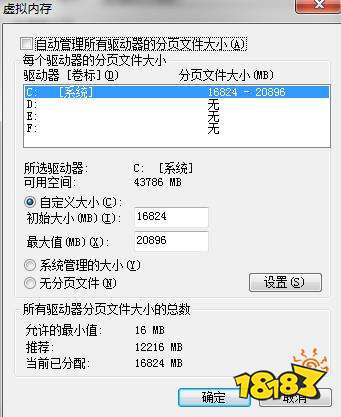
By default, most operating systems create a paging file automatically. However, you can adjust the size of the paging file to optimize system performance. Here’s how you can create and manage a paging file:
-
On Windows, go to the Control Panel, click on System, and then select “Advanced system settings.” In the System Properties window, go to the “Advanced” tab, and click on “Settings” under the “Performance” section. In the Performance Options window, go to the “Advanced” tab, and click on “Change” under the “Virtual memory” section. Here, you can adjust the size of the paging file.
-
On macOS, go to the Apple menu, click on “System Preferences,” and then select “Memory.” In the Memory tab, you can see the current size of the paging file and adjust it if needed.
The Benefits of Using a Paging File
Using a paging file offers several benefits:
-
Increased system performance: By providing additional virtual memory, the operating system can run more applications simultaneously without crashing or slowing down.
-
Improved multitasking: The paging file allows you to switch between applications more smoothly, as the operating system can quickly load and save data to the virtual memory.
-
Enhanced system stability: By managing excess data, the operating system can prevent crashes and errors that may occur when the RAM is full.
The Drawbacks of Using a Paging File
While the paging file offers many benefits, it also has some drawbacks:
-
Slower performance: Accessing data from the hard drive is slower than accessing data from RAM. Therefore, using a large paging file can slow down your system.
-
Increased wear and tear on the hard drive: Frequent reading and writing to the paging file can cause additional wear and tear on your hard drive, potentially shortening its lifespan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a paging file is a vital component of modern operating systems. It allows your computer to use a portion of your hard drive as virtual memory, enhancing system performance and stability. While there are some drawbacks to consider, the benefits of using a paging file often outweigh the negatives. By understanding how a paging file works and how to manage it, you can optimize your system’s performance and ensure a smooth computing experience.
| Operating System | Location of Paging File | Default Size |
|---|---|---|
Related Stories |




