
DXF File: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
Are you looking to delve into the world of DXF files? If so, you’ve come to the right place. DXF files, or Drawing Exchange Format files, are widely used in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. They are a crucial component for sharing and exchanging design data between different software applications. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of DXF files, from their history to their applications, and everything in between.
Understanding the Basics of DXF Files
DXF files are a type of vector file format that was developed by Autodesk. They were created to facilitate the exchange of design data between different CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software applications. The format was first introduced in 1982, and since then, it has become a de facto standard in the industry.
One of the key features of DXF files is their ability to store a wide range of geometric entities, such as lines, arcs, circles, and text. This makes them highly versatile and suitable for various design purposes. Additionally, DXF files can be easily opened and edited in most CAD software applications, making them a popular choice for designers and engineers.
Creating and Editing DXF Files
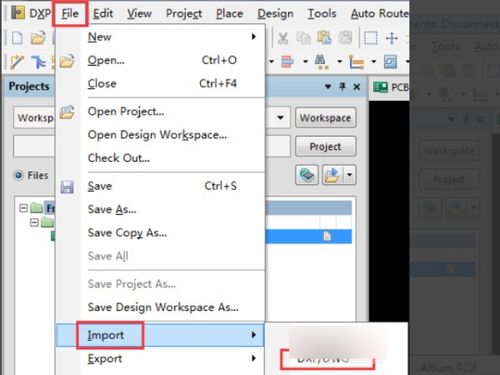
Creating a DXF file is a straightforward process. Most CAD software applications offer the option to export files in DXF format. To create a DXF file, simply open your design in the CAD software, go to the export or save as option, and select DXF as the file format.
Editing DXF files is also quite simple. You can open a DXF file in any CAD software that supports the format. Once opened, you can make changes to the design, such as modifying the geometry, adding or removing elements, and updating the properties of the objects.
Applications of DXF Files
DXF files are used in a wide range of industries and applications. Here are some of the most common uses:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Architecture | Designing buildings, structures, and interiors |
| Engineering | Creating technical drawings and schematics |
| Construction | Planning and managing construction projects |
| Manufacturing | Designing and producing products |
| Product Design | Developing new products and prototypes |
These are just a few examples of the many applications of DXF files. The versatility of the format makes it an essential tool for professionals in various fields.
Compatibility and Interoperability
One of the strengths of DXF files is their compatibility with a wide range of CAD software applications. This makes it easy for designers and engineers to share and exchange design data without worrying about compatibility issues.
However, it’s important to note that while DXF files are widely supported, there may be some limitations in terms of interoperability. For example, certain advanced features or custom properties may not be fully supported in all CAD software applications. It’s always a good idea to check the compatibility of the software you’re using with the DXF files you’re working with.
Best Practices for Working with DXF Files
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when working with DXF files:
- Always save your original design in its native CAD format before exporting it as a DXF file.
- Use a standard DXF file version to ensure compatibility with different software applications.
- Keep your DXF files organized and well-documented to make them easier to manage and share.
- Regularly update your CAD software to take advantage of the latest features and improvements.
Conclusion
DXF files are an essential tool for professionals in the architecture, engineering, and construction industries. Their versatility, compatibility, and ease of use make them a popular choice for sharing and exchanging design data. By






