
Understanding the .wav File Sampled at 48kHz: A Detailed Overview
When it comes to audio files, the .wav format is one of the most widely used and recognized. But what does it mean when you see that a file is sampled at 48kHz? Let’s delve into the details and explore the significance of this sampling rate in the context of .wav files.
What is a .wav File?

The .wav file format, also known as Pulse Code Modulation (PCM), is a standard audio file format developed by Microsoft and IBM. It is widely used for storing audio data in uncompressed, high-quality format. Unlike compressed audio formats like MP3, .wav files do not lose any audio quality during compression, making them ideal for professional audio editing and production.
Understanding Sampling Rate
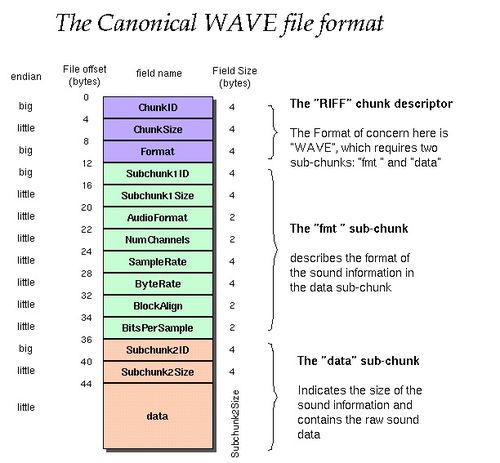
Sampling rate refers to the number of samples taken per second in an audio file. These samples represent the audio signal at different points in time. The higher the sampling rate, the more accurately the audio signal is captured. Common sampling rates include 44.1kHz, 48kHz, and 96kHz.
The Significance of 48kHz Sampling Rate
Now, let’s focus on the 48kHz sampling rate. This particular sampling rate is widely used in various audio applications due to its balance between quality and file size. Here are some key reasons why 48kHz is a popular choice:
-
Professional Audio Standards: Many professional audio devices and software are designed to work with 48kHz sampling rates. This ensures compatibility and seamless integration in professional workflows.
-
CD Quality: The 48kHz sampling rate is close to the standard CD quality of 44.1kHz. This means that files sampled at 48kHz can be easily converted to CD quality without significant loss in audio quality.
-
Reduction in File Size: While 48kHz is a higher sampling rate than 44.1kHz, it still offers a good balance between quality and file size. This makes it suitable for applications where storage space is a concern, such as streaming or online distribution.
-
Studio Workflows: Many recording studios use 48kHz sampling rates for their projects. This ensures consistency and compatibility across different stages of the production process.
Table: Comparison of Sampling Rates
| Sampling Rate | Frequency Range | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| 44.1kHz | 20Hz – 20kHz | CD Quality, Consumer Audio |
| 48kHz | 20Hz – 20kHz | Professional Audio, Studio Workflows |
| 96kHz | 20Hz – 40kHz | High-Resolution Audio, Critical Listening |
As you can see from the table, the 48kHz sampling rate offers a wide frequency range, covering the audible spectrum for most listeners. This makes it suitable for a wide range of audio applications, from professional recording to consumer use.
How to Convert to 48kHz Sampling Rate
Converting an audio file to 48kHz sampling rate is a straightforward process. Most audio editing software, such as Audacity or Adobe Audition, allows you to resample audio files. Here’s a general guide on how to do it:
-
Open the audio file in your preferred audio editing software.
-
Locate the ‘Resample’ or ‘Sample Rate’ option in the software’s menu.
-
Select ’48kHz’ as the new sampling rate.
-
Save the converted file.
It’s important to note that converting an audio file to a different sampling rate may introduce some artifacts, especially if the original file was not recorded at the desired sampling rate. Therefore, it’s always recommended to record audio at the intended sampling rate for the





