
Understanding Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Are you struggling with overwhelming debt? Filing for bankruptcy might be a viable option for you. One of the most common types of bankruptcy is Chapter 7. This article will guide you through the process of how to file bankruptcy under Chapter 7, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the steps involved.
What is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
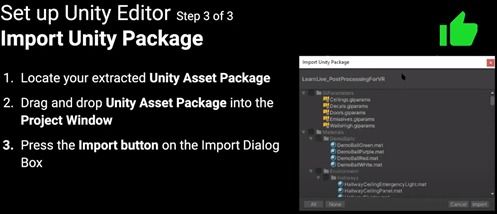
Chapter 7 bankruptcy, also known as liquidation bankruptcy, is designed for individuals who have little to no disposable income. It allows you to discharge most of your unsecured debts, such as credit card debt, medical bills, and personal loans. However, certain debts, like student loans, alimony, and child support, are not eligible for discharge.
Eligibility for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
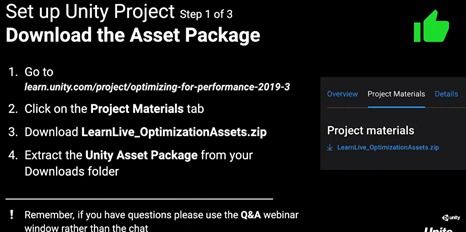
Before you can file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you must meet certain eligibility requirements. One of the most crucial requirements is passing the means test. The means test evaluates your income and expenses to determine if you qualify for Chapter 7. If your income is below the state median, you automatically pass the means test. If your income is above the median, you must subtract certain expenses from your income to determine if you have disposable income. If you have no disposable income, you may still qualify for Chapter 7.
Steps to File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
Now that you understand the basics of Chapter 7 bankruptcy, let’s dive into the steps involved in filing for it:
-
Find a bankruptcy attorney: It’s highly recommended to consult with a bankruptcy attorney before filing for bankruptcy. They can help you navigate the process and ensure that your rights are protected.
-
Complete credit counseling: Before you can file for bankruptcy, you must complete a credit counseling course from an approved provider. This course will help you understand your financial situation and explore alternatives to bankruptcy.
-
Prepare your bankruptcy petition: Your bankruptcy attorney will assist you in preparing your bankruptcy petition, which includes detailed information about your financial situation, debts, assets, and income.
-
File your bankruptcy petition: Once your petition is complete, your attorney will file it with the bankruptcy court. You will also need to pay a filing fee, which varies by state.
-
Attend the meeting of creditors: Approximately 30 to 60 days after filing your petition, you will need to attend a meeting of creditors. This meeting is typically brief and serves as an opportunity for creditors to ask you questions about your financial situation.
-
Wait for your discharge: After the meeting of creditors, the bankruptcy court will review your case. If everything is in order, the court will issue a discharge order, which will eliminate your eligible debts.
What Happens to Your Property?
One of the most common concerns when filing for bankruptcy is what will happen to your property. Under Chapter 7 bankruptcy, certain assets are exempt from liquidation, meaning you can keep them. Exemptions vary by state, but common exempt assets include your primary residence, personal belongings, and retirement accounts. However, if you have non-exempt assets, the bankruptcy trustee may sell them to pay off your creditors.
Impact on Your Credit
Filing for bankruptcy will have a significant impact on your credit score. It will remain on your credit report for up to 10 years, depending on the type of bankruptcy you file. However, it’s important to note that bankruptcy can provide a fresh start and allow you to rebuild your credit over time.
Alternatives to Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
While Chapter 7 bankruptcy can be a valuable tool for debt relief, it’s not the only option available. Depending on your financial situation, you may consider other alternatives, such as Chapter 13 bankruptcy, debt consolidation, or credit counseling.
Conclusion
Filing for bankruptcy under Chapter 7 can be a complex process, but it can also provide much-needed relief from overwhelming debt. By understanding the eligibility requirements, steps involved, and potential consequences, you can make an informed decision about whether Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the right choice for you.



