
Windows Host File Location: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
Understanding the location of the Windows host file is crucial for anyone looking to manage their network connections more effectively. The host file is a fundamental component of the Windows operating system that maps hostnames to IP addresses. By modifying this file, you can control how your computer resolves domain names, which can be particularly useful for bypassing certain restrictions or speeding up your internet experience. Let’s delve into the details of where this file is located and how to access it.
Where is the Windows Host File Located?
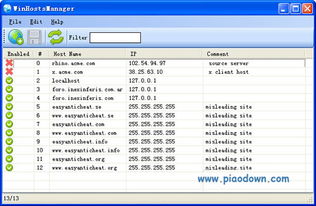
The Windows host file is typically located in the following directory:
| Windows Version | Host File Location |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 and Windows 11 | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| Windows 7 | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| Windows Vista | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| Windows XP | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
As you can see, the location of the host file remains consistent across different versions of Windows. However, it’s important to note that you may need administrative privileges to access and modify this file.
Accessing the Windows Host File
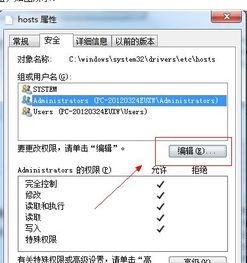
Accessing the Windows host file is a straightforward process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Open File Explorer by pressing the Windows key + E.
- In the address bar, type the following path: C:WindowsSystem32driversetc.
- Press Enter, and you should see the hosts file listed in the directory.
- Right-click on the hosts file and select “Open with.”
- In the “Open with” dialog box, choose a text editor that you trust, such as Notepad, and click “OK.”
Once you have opened the hosts file, you can begin editing it. Be cautious when making changes, as incorrect entries can cause network connectivity issues.
Understanding the Hosts File Format
The Windows host file is a plain text file, which means it can be opened and edited with any text editor. Each line in the file represents a mapping between a hostname and an IP address. The format of a typical line is as follows:
IP Address Hostname [Alias…]
For example:
127.0.0.1 localhost
This line maps the IP address 127.0.0.1 to the hostname “localhost,” which is a common entry in the host file.
Modifying the Hosts File
Modifying the Windows host file can be useful for various purposes, such as:
- Bypassing DNS restrictions: By mapping a restricted domain to a local IP address, you can bypass DNS-based restrictions.
- Speeding up internet experience: By mapping frequently visited domains to their IP addresses, you can reduce the time it takes for your computer to resolve domain names.
- Testing new websites: Before launching a new website, you can map its domain to a local IP address to test it without affecting your live network connections.
When modifying the host file, ensure that you follow the correct format and double-check your entries. Incorrect entries can lead to network connectivity issues, so it’s essential to be cautious.
Restoring the Original Hosts File
In case you make a mistake while editing the host file, it’s important to know how to restore the original file. Here’s how you can do it:





