
As a tax filer, navigating the complexities of tax laws and regulations can be a daunting task. Whether you’re an expatriate, a small business owner, or simply someone looking to ensure compliance with tax obligations, understanding the ins and outs of tax filing is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, providing you with the knowledge and resources needed to become an informed and confident tax filer.
Understanding Your Tax Obligations

Your tax obligations depend on various factors, including your residency status, income sources, and the countries you are taxed in. Here’s a breakdown of some key considerations:
| Residency Status | Income Sources | Tax Jurisdictions |
|---|---|---|
| Resident | Wages, salaries, dividends, interest, and rental income | Both the country of residence and the country of citizenship |
| Non-resident | Income earned in the country of residence | Only the country of residence |
Choosing the Right Tax Filing Method
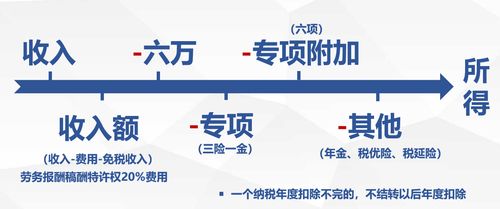
Selecting the appropriate tax filing method is essential to ensure accurate reporting and compliance. Here are some common filing methods:
- Standard Deduction: This method allows you to deduct a fixed amount from your taxable income, reducing your overall tax liability.
- Itemized Deductions: If you have significant deductible expenses, such as mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions, itemizing may be more beneficial.
- Zero-Balance Filing: This method is suitable for individuals with no taxable income, such as students or those receiving unemployment benefits.
Organizing Your Tax Documents
Properly organizing your tax documents is crucial for a smooth filing process. Here’s a list of essential documents to gather:
- W-2 or 1099 forms from employers
- Bank statements and investment account statements
- Medical expense receipts
- Property tax bills
- Charitable donation receipts
Using Tax Software or Hiring a Professional
Deciding whether to use tax software or hire a professional depends on your comfort level, expertise, and the complexity of your tax situation. Here are some factors to consider:
- Tax Software: Offers convenience, affordability, and step-by-step guidance. Ideal for individuals with straightforward tax situations.
- Professional Tax Preparer: Provides personalized advice, expertise, and peace of mind. Suitable for individuals with complex tax situations or those seeking a higher level of assurance.
Understanding Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax credits and deductions can significantly reduce your tax liability. Here are some common tax credits and deductions:
- Child Tax Credit: A refundable credit for qualifying children under the age of 17.
- Retirement Account Contributions: Contributions to retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s may be deductible.
- Medical Expense Deduction: Deductible medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income.
Deadlines and Penalties
Missing tax filing deadlines or failing to pay taxes on time can result in penalties and interest. Here are some key deadlines and penalties:
- April 15: Deadline for filing individual tax returns in the United States.
- October 15: Deadline for filing an extension if you haven’t filed your tax return by April 15.
- Penalties: Failure to file penalties, failure to pay penalties, and interest on late payments.
Seeking Professional Advice
When in doubt, seeking professional advice is always a wise decision. Tax professionals can provide personalized guidance, help you navigate complex tax situations, and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
By understanding your tax obligations, choosing the right filing method, organizing your tax






