
Windows Hosts File Location: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
Understanding the location of the Windows hosts file is crucial for anyone looking to manage their computer’s network settings. This file plays a significant role in how your computer handles domain names and IP addresses. In this guide, we will delve into the details of finding the Windows hosts file, its importance, and how to edit it safely.
Where is the Windows Hosts File Located?
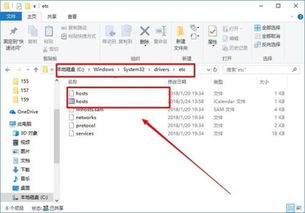
The Windows hosts file is typically located in the following directory:
| Windows Version | Location |
|---|---|
| Windows 10, 8, 7, and Vista | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
| Windows XP | C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts |
It’s important to note that the hosts file is a plain text file, which means you can open and edit it using any text editor. However, be cautious when making changes, as incorrect entries can disrupt your internet connectivity.
Why is the Windows Hosts File Important?
The Windows hosts file serves as a local DNS resolver. When you type a domain name into your web browser, the hosts file is checked first to see if it has a corresponding IP address. If it does, your computer will use that IP address instead of querying a DNS server. This can be useful for several reasons:
-
Speeding up internet access by bypassing DNS lookups.
-
Blocking access to certain websites by redirecting their domain names to a local IP address (e.g., 127.0.0.1).
-
Testing new websites or services without changing your DNS settings.
How to Edit the Windows Hosts File

Editing the Windows hosts file is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to follow these steps carefully to avoid any issues:
-
Open the hosts file using a text editor. You can use Notepad, Notepad++, or any other text editor of your choice.
-
Make the necessary changes to the file. Each line in the hosts file contains an IP address and a domain name, separated by a space. For example:
-
127.0.0.1 example.com -
Save the file after making changes. Ensure that you save it with the .txt extension, not .docx or any other format.
-
Restart your computer or flush the DNS cache to apply the changes. You can flush the DNS cache by opening the Command Prompt as an administrator and typing:
-
ipconfig /flushdns
Common Uses of the Windows Hosts File
Here are some common scenarios where editing the Windows hosts file can be beneficial:
-
Blocking Websites: Redirecting a website’s domain name to a local IP address (e.g., 127.0.0.1) can block access to that website.
-
Testing Websites: Redirecting a domain name to a different IP address can help you test a new website or service without changing your DNS settings.
-
Speeding Up Internet Access: Bypassing DNS lookups by using the hosts file can speed up internet access, especially if you have a slow DNS server.
Conclusion
Understanding the location and purpose of the Windows hosts file is essential for managing your computer’s network settings. By editing the hosts file, you can block websites, test new services, and potentially speed up your internet access. Always exercise caution when making changes to the hosts file, as incorrect entries can disrupt your internet connectivity.






