
BMP Image File: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you curious about the BMP image file format? Do you want to understand its intricacies and how it differs from other image formats? Look no further! This article will delve into the details of the BMP image file, exploring its history, technical specifications, and practical applications. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of what makes BMP files unique and why they are still widely used today.
History of BMP
The BMP (Bitmap) image file format was developed by Microsoft in 1980. It was designed to be a simple, uncompressed image format that could be used across different platforms and applications. Initially, BMP files were primarily used in Windows operating systems, but they have since become a standard image format used by various software and devices.
Technical Specifications
BMP files are stored in a bitmap format, which means that each pixel in the image is represented by a specific color value. This format is uncompressed, which means that the file size is directly proportional to the image’s resolution and color depth. Here are some key technical specifications of BMP files:
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| File Extension | .bmp |
| Color Depth | 1 to 32 bits per pixel |
| Compression | None |
| File Format | Bitmap |
One of the advantages of BMP files is their simplicity. They do not require any additional metadata or information to be stored within the file, making them easy to work with and compatible with a wide range of software and devices.
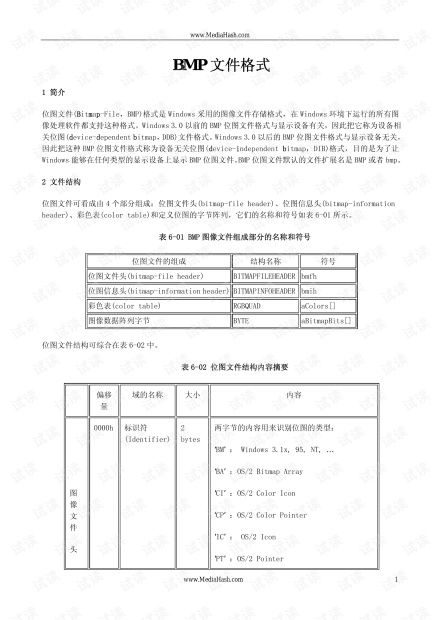
File Structure
The BMP file structure consists of several components, including the file header, image header, and pixel data. Here’s a brief overview of each component:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| File Header | Contains information about the file’s size, offset to the pixel data, and other metadata. |
| Image Header | Contains information about the image’s dimensions, color depth, and compression method (if any). |
| Pixel Data | Contains the actual pixel values that make up the image. |
The file header is the first 14 bytes of the BMP file and contains information about the file’s size, offset to the pixel data, and other metadata. The image header follows the file header and contains information about the image’s dimensions, color depth, and compression method (if any). Finally, the pixel data is the actual image content, stored in a row-major order.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any image format, BMP files have their advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a comparison of some of the key pros and cons:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy to work with | Uncompressed, resulting in large file sizes |
| High-quality images | Not suitable for web use due to large file sizes |
| Wide compatibility | Not optimized for performance |
While BMP files are not ideal for web use due to their large file sizes, they are still widely used in various applications, such as graphic design, photography, and medical imaging. Their simplicity and high-quality images make them a popular choice for professionals who require precise control over their images.





