
Understanding the IRS Tax Extension: A Comprehensive Guide for You
When it comes to filing taxes, the IRS offers a valuable tool known as the tax extension. This guide will delve into the details of what a tax extension is, how to apply for one, and the benefits it provides. Whether you’re a seasoned tax filer or new to the process, this information will help you navigate the complexities of tax extensions.
What is an IRS Tax Extension?

An IRS tax extension is an extension of the time you have to file your tax return. It is not an extension of the time to pay your taxes. By filing for an extension, you can delay the deadline for filing your tax return from the original due date to October 15th.
Who Can Apply for an IRS Tax Extension?
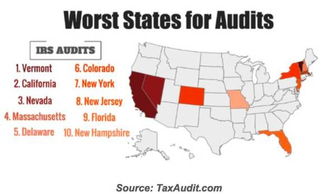
Almost anyone who needs more time to file their tax return can apply for an IRS tax extension. This includes individuals, partnerships, corporations, estates, and trusts. However, there are some exceptions, such as estates and trusts that are required to file an estate tax return.
How to Apply for an IRS Tax Extension

Applying for an IRS tax extension is a straightforward process. You can apply for an extension by filing Form 4868, Application for Automatic Extension of Time to File U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, with the IRS. Here’s how to do it:
-
Fill out Form 4868. You can find the form on the IRS website or request it by calling the IRS at 1-800-829-1040.
-
Submit the form to the IRS by the original filing deadline, which is April 15th. You can submit the form online, by mail, or by fax.
-
Pay any taxes owed by the original filing deadline. If you can’t pay the full amount, you can pay as much as you can to avoid penalties and interest.
Benefits of an IRS Tax Extension
There are several benefits to filing for an IRS tax extension:
-
More Time to File: An extension gives you an additional six months to gather your tax documents, calculate your taxes, and file your return.
-
Peace of Mind: Knowing that you have more time to file can reduce stress and help you avoid late filing penalties.
-
Penalty Avoidance: If you file for an extension and pay any taxes owed by the original filing deadline, you can avoid late filing penalties.
Penalties for Not Filing on Time
It’s important to note that while an extension gives you more time to file, it does not give you more time to pay your taxes. If you don’t file your tax return by the original due date and you owe taxes, you may be subject to penalties and interest.
| Penalty Type | Percentage | Applies to |
|---|---|---|
| Late Filing Penalty | 5% of the tax owed per month (up to 25%) | Unfiled tax returns |
| Late Payment Penalty | 0.5% of the tax owed per month (up to 25%) | Unpaid taxes |
Common Questions About IRS Tax Extensions
Here are some common questions about IRS tax extensions:
-
Can I file for an extension if I haven’t received all my tax documents?
Yes, you can file for an extension even if you haven’t received all your tax documents. Just estimate the amount of tax you owe and file your extension.
-
Do I have to pay interest on the taxes I owe if I file for an extension?
No, you do not have to pay interest on the taxes you owe if you file for an extension. However, if you don’t pay the taxes you owe by the original filing deadline, you may be subject to interest on the unpaid amount.





