
FTP File Transfer Protocol: A Comprehensive Guide for Users
FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of files between a client and a server on a computer network. It’s been around for decades and remains a vital tool for many businesses and individuals. In this detailed guide, we’ll explore the ins and outs of FTP, covering its history, how it works, its benefits, and its limitations.
History of FTP
FTP was developed in the 1970s by the Network Working Group (NWG) as a means to transfer files between computers on the ARPANET, the precursor to the modern internet. The first version of FTP was released in 1971, and it quickly became a standard for file transfer. Over the years, several versions of FTP have been released, with the most recent being FTP over SSL (FTPS) and FTP over TLS (FTPS). These newer versions provide enhanced security features to protect sensitive data during transfer.
How FTP Works
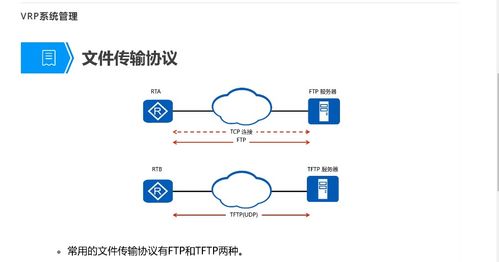
FTP operates on a client-server model. The client, which can be a computer or a mobile device, initiates a connection to the server. Once the connection is established, the client can send commands to the server to upload, download, delete, or rename files. The server responds to these commands and performs the requested actions. The communication between the client and server is done using a series of commands and responses, which are standardized in the FTP protocol.
Here’s a basic overview of the FTP process:
- The client connects to the server using a username and password.
- The client sends a command to the server, such as “list” to view the files on the server.
- The server responds with the requested information.
- The client sends another command, such as “get” to download a file.
- The server sends the file to the client.
- The client receives the file and saves it to the local machine.
Benefits of Using FTP

FTP offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for file transfer:
- Speed: FTP is designed for fast file transfer, making it ideal for large files and bulk data transfers.
- Reliability: FTP is a robust protocol that can handle large files and multiple connections without issues.
- Security: With the introduction of FTPS, users can now encrypt their data during transfer, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure.
- Compatibility: FTP is supported by a wide range of operating systems and devices, making it accessible to users worldwide.
- Flexibility: FTP allows users to transfer files in various formats, including text, binary, and ASCII.
Limitations of FTP
While FTP is a powerful tool, it also has some limitations:
- Security Concerns: Without encryption, FTP is not secure, and sensitive data can be intercepted by unauthorized users.
- Complexity: FTP can be complex for new users, requiring knowledge of commands and file management.
- Bandwidth Limitations: FTP can consume a significant amount of bandwidth, which may be a concern for organizations with limited resources.
FTP vs. Other File Transfer Methods
When it comes to file transfer, there are several alternatives to FTP, such as:
- HTTP/HTTPS: These protocols are commonly used for web browsing and can be used for file transfer, but they are not as efficient as FTP for large files.
- SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol): SFTP is a more secure alternative to FTP, using SSH for encryption. However, it can be slower than FTP due to the encryption process.
- FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS): FTPS is a secure version of FTP that uses SSL or TLS for encryption. It offers the benefits of FTP with enhanced security features.
Setting Up an FTP Server
Setting up an FTP server is a straightforward process, but it requires some technical knowledge. Here’s a basic outline of the steps involved:
- Choose an FTP Server Software: There are several FTP server software options available, such as




