
Path to Windows Host File: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Windows Host file is crucial for anyone looking to manage their network connections more effectively. This guide will walk you through the ins and outs of the Windows Host file, providing you with a detailed, multi-dimensional introduction.
What is the Windows Host File?
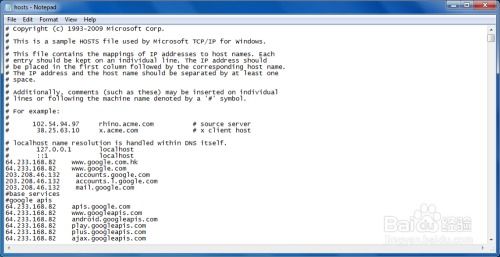
The Windows Host file is a crucial component of the Windows operating system. It is a simple text file that maps hostnames to IP addresses. When you type a website’s name into your browser, the operating system checks the Host file to see if it has an associated IP address. If it does, the system uses that IP address to connect to the website. If not, it queries the DNS server to resolve the hostname to an IP address.
Locating the Windows Host File
By default, the Windows Host file is located at C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts. However, you can find it by following these steps:
- Open File Explorer.
- Click on the “View” tab at the top of the window.
- Check the “Hidden items” box in the “Show/hide” section.
- Scroll down to the “Windows” folder and open it.
- Open the “System32” folder.
- Open the “drivers” folder.
- Open the “etc” folder, and you’ll find the Host file there.
Editing the Windows Host File
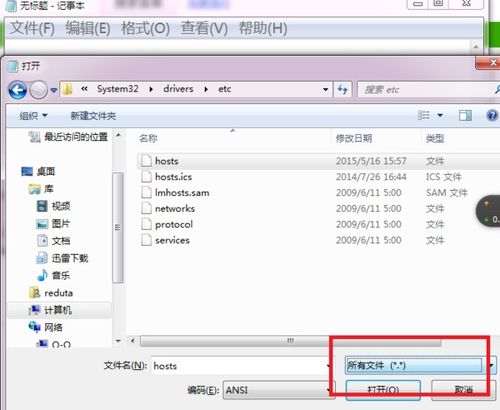
Editing the Windows Host file requires administrative privileges. Here’s how to do it:
- Right-click on the Host file and select “Open with.”
- Select “Notepad” or any other text editor you prefer.
- Make sure to open the file as an administrator. If you’re using Notepad, you’ll see a prompt asking for administrative privileges. Click “Yes.”
Once the file is open, you can add or remove entries. Each entry consists of an IP address followed by a space and the hostname. For example:
192.168.1.1 www.example.com
Understanding Host File Entries
Here’s a breakdown of the components of a Host file entry:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| IP Address | The IP address associated with the hostname. |
| Hostname | The domain name or website you want to map to the IP address. |
Common Uses of the Windows Host File
The Windows Host file has several practical uses:
- Blocking Websites: You can block access to certain websites by adding their domain names to the Host file and mapping them to a non-existent IP address.
- Testing Local Websites: When developing a website, you can map the domain name to your local IP address to test it without needing to set up a DNS server.
- Speeding Up DNS Resolution: By caching DNS entries in the Host file, you can reduce the time it takes to resolve domain names.
Example of a Modified Host File
Here’s an example of a modified Host file that blocks access to some popular social media websites:
0.0.0.0 www.facebook.com 0.0.0.0 www.twitter.com 0.0.0.0 www.instagram.com
Conclusion
The Windows Host file is a powerful tool that can help you manage your network connections and customize your browsing experience. By understanding how to locate, edit, and use the Host file, you can take full advantage of its features and benefits.





