
Understanding Ohio Income Tax: A Comprehensive Guide for You
When it comes to managing your finances, understanding the intricacies of Ohio income tax is crucial. Whether you’re a resident or a visitor, knowing how the tax system works can help you make informed decisions. In this detailed guide, we’ll delve into various aspects of Ohio income tax, ensuring you have a comprehensive understanding.
Who Needs to Pay Ohio Income Tax?
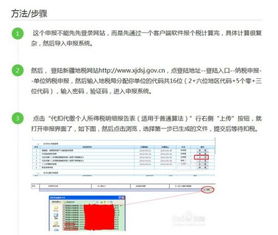
Ohio income tax applies to individuals, estates, and trusts that have income from sources within the state. This includes both residents and non-residents who earn income in Ohio. If you earn income in Ohio, you are generally required to file an Ohio income tax return, regardless of where you live.
Resident vs. Non-Resident
It’s important to differentiate between residents and non-residents when it comes to Ohio income tax. A resident is someone who has lived in Ohio for more than six months in a calendar year. Non-residents, on the other hand, are individuals who have lived in Ohio for less than six months in a calendar year.
Ohio Income Tax Rates
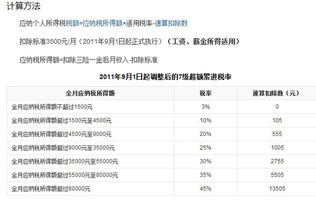
Ohio income tax rates vary depending on your filing status and taxable income. The rates are progressive, meaning the higher your income, the higher the tax rate. Here’s a breakdown of the rates for the 2021 tax year:
| Income Range | Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 – $10,000 | 0.75% |
| $10,001 – $25,000 | 1.5% |
| $25,001 – $50,000 | 2.25% |
| $50,001 – $100,000 | 2.75% |
| $100,001 – $150,000 | 3.25% |
| $150,001 – $200,000 | 3.75% |
| $200,001 and above | 4.75% |
Exemptions and Deductions
Ohio offers various exemptions and deductions that can help reduce your taxable income. Some common deductions include:
- Standard Deduction: The standard deduction for the 2021 tax year is $4,500 for single filers and $9,000 for married filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: You can claim a personal exemption for yourself, your spouse, and each dependent you claim on your federal tax return.
- Retirement Account Contributions: Contributions to certain retirement accounts, such as IRAs and 401(k)s, may be deductible.
- Medical Expenses: If you itemize deductions, you may be able to deduct eligible medical expenses that exceed 7.5% of your adjusted gross income.
Filing Your Ohio Income Tax Return
There are several ways to file your Ohio income tax return, including online, by mail, or through a tax preparer. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Online Filing: The Ohio Department of Taxation offers an online filing option through its website. This is the most convenient and fastest way to file your return.
- By Mail: You can file your return by mail using Form IT-1040. Be sure to follow the instructions carefully to ensure your return is processed correctly.
- Tax Preparer: If you prefer, you can have a tax preparer file your return on your behalf. Make sure to choose a reputable preparer and keep all documentation related to your return.
Deadlines and Penalties
It’s important to be aware of the deadlines and potential penalties associated with Ohio income tax:
- Deadline: The deadline for filing your Ohio income tax return is April 15th, unless it falls on a weekend or holiday, in which case the deadline is extended to the following Monday.





